Reconnecting the Disconnected: UA Physiology Professor Receives $1.2M NIH Grant to Use AI to Restore Movement in Paralyzed Limbs
When a person is paralyzed by a stroke or an injury, the brain and the neuron networks that control movement become disconnected from the muscles. Dr. Andrew Fuglevand is using artificial intelligence to stimulate multiple muscles to elicit natural moveme


Andrew Fuglevand, PhD
If any of these signals are blocked or broken, such as from a spinal cord injury or stroke, the messages from the brain to the muscles are unable to connect, causing paralysis. The person’s muscles are functional, but they no longer are being sent instructions.
Andrew Fuglevand, PhD, professor of physiology at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson and professor of neuroscience at the UA College of Science, has received a $1.2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to study electrical stimulation of the muscles as a way to restore limb movements in paralyzed individuals. Dr. Fuglevand’s goal is to restore voluntary movement to a person’s own limbs rather than relying on external mechanical or robotic devices.
Producing a wide range of movements in paralyzed limbs has been unsuccessful so far because of the substantial challenges associated with identifying the patterns of muscle stimulation needed to elicit specified movements, Dr. Fuglevand explained.
"Moving a finger involves as many as 20 different muscles at a time. Moving an arm can involve more than 50 different muscles. They all work together in an intricate 'dance' to produce beautifully smooth movements. Replicating how the brain naturally coordinates the activities of these muscles is extremely challenging," he said.
This is where recent advances in “machine learning,” or artificial intelligence (AI), is making the impossible become possible. Dr. Fuglevand, who also is an affiliate professor of biomedical engineering and teaches neuroscience courses at the UA, is employing machine learning to mimic and replicate the patterns of brain activity that control groups of muscles. Tiny electrodes implanted in the muscles replay the artificially generated signals to produce complex movements.
"
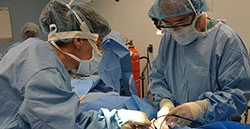
Dr. Fuglevand (right) with physiology professor Dr. Katalin Gothard implanting electrodes in paralyzed muscles.
"More than 5 million Americans are living with some form of paralysis, and the leading causes are stroke and spinal injury," said Nicholas Delamere, PhD, head of the UA Department of Physiology. "New innovations in artificial intelligence, developed by scientists like Dr. Fuglevand and his team, are allowing them to decode subtle brain signals and make brain-machine interfaces that ultimately will help people move their limbs again."
"The headway researchers have made in our understanding of artificial intelligence, machine learning and the brain is incredible," said UA President Robert C. Robbins, MD. "The opportunity to incorporate AI to brain-limb communication has life-changing potential, and while there are many challenges to optimize these interventions, we are really committed to making this step forward. I am incredibly excited to track Dr. Fuglevand's progress with this new grant."

Muscle electrodes and movement sensors used to characterize the control of finger movements.
Research reported in this release was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, under grant No. 1R01NS102259-01A1. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
About the UA College of Medicine – Tucson
The University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson is shaping the future of medicine through state-of-the-art medical education programs, groundbreaking research and advancements in patient care in Arizona and beyond. Founded in 1967, the college boasts more than 50 years of innovation, ranking among the top medical schools in the nation for research and primary care. Through the university's partnership with Banner Health, one of the largest nonprofit health-care systems in the country, the college is leading the way in academic medicine. For more information, please visit medicine.arizona.edu.

