UArizona Health Sciences Researchers Find Biomarker that Can Appear Before Stomach Cancer Develops
A microRNA that can be found in a blood sample may make it easier to detect gastric cancer and could lead to improved treatment for diseases that are resistant to common immunotherapies.
Video: How a blood sample may make it easier to detect gastric cancers and could lead to improved treatments for cancers that are resistant to common immunotherapies.
A promising new biomarker that appears in patients before stomach cancer develops may help with early detection of the disease and improve patient response to therapy, according to findings in a study led by University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers.
The biomarker can be detected through a simple blood test, saving time and lowering costs. Currently, stomach cancer diagnosis requires endoscopic collection of stomach tissue through a biopsy procedure, and then analysis by pathology.
Published in Gut, the journal of the British Society of Gastroenterology, the study was led by Juanita L. Merchant, MD, PhD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the UArizona College of Medicine – Tucson, a cancer biology program researcher at the UArizona Cancer Center and an elected member of the National Academy of Medicine.

Juanita Merchant, MD, PhD, is a gastric cancer expert whose research focuses on the molecular mechanisms of the disease.
The biomarker, MiR130b, is a microRNA – or small non-coding RNA molecule that can play an important role in regulating gene expression, affecting disease development and progression. MiR130b can be produced by a group of immune cells called myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), commonly associated with infections caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a bacteria associated with ulcers. These particular cell types in the stomach correlate with early, preneoplastic changes (before a tumor develops) that can lead to gastric cancer long after an H. pylori infection has passed.
The study included collaboration with Yana Zavros, PhD, associate head for research in the College of Medicine – Tucson’s Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine and the Cancer Center’s shared resource director for Tissue Acquisition Cellular and Molecular Analysis.
“Even though you get can get rid of the bacteria, oftentimes the infection itself already has initiated a cascade of events that inevitably may lead to cancer,” Dr. Zavros said. “That is why early detection is so important.”
A Blood Test Instead of a Procedure
The study arose out of basic science mouse models that simulated changes in the stomach similar to that caused by H. pylori. This led the researchers to identify MiR130b in the mouse models, and they also detected the same microRNA in the plasma of human patients that either had precancerous changes or those that already had progressed to cancer.
“This was a retrospective study,” said Dr. Merchant, who is a member of the university’s BIO5 Institute. “It is very exciting because now we can begin looking at this biomarker more prospectively in different patient populations.”
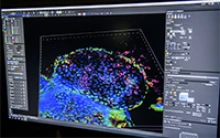
Imaging shows H. pylori infection in gastric organoids, which are miniature organs with realistic microanatomy that were developed in a lab from tissue samples.
Although less common in the United States, the National Cancer Institute reports gastric (stomach) cancer is the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. The findings, however, could have major implications for Arizona’s rural areas and Hispanic and Native American populations, which are at greater risk for developing gastric and other gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, because these diseases often are caused by dietary and environmental factors and may go undetected for long periods.
Dr. Merchant’s lab has a “sub-project” in the Cancer Center’s U54 grant (Partnership for Native American Cancer Prevention) to study detection of the microRNA described in the Gut paper in members of Native American populations with H. pylori.
“This molecular signature (the microRNA – MiR130b) that we discovered may help us see if patients have changes in their mucosa (the membrane that lines the stomach) related to having H. pylori,” Dr. Merchant said. “And a blood sample would be less invasive and then could be a way to make the decision whether we need to bring a patient in for an endoscopy.”
Broader Implications for Treatment
Once diagnosed, gastric cancer can be difficult to treat. Immunotherapies with proven effectiveness in treating other types of cancer are not as successful against most GI cancers, including stomach cancer. The researchers believe these new findings in gastric cancer may help to address why other GI cancers also are resistant to therapy.
“The underlying mechanism by which a patient may not respond well in gastric cancer may be applicable in other organs as well” Dr. Zavros said. “The way the cells interact with each other to render that patient resistant to therapy may be quite similar between gastric, pancreatic and colon cancers.”

Yana Zavros, PhD, studies cancer and immune cells as part of her research into H. pylori-induced diseases.
Dr. Merchant added: “There may be dual-purposes. We can look at it as a biomarker to help us from a diagnostic perspective, but we also can look at therapies that can be developed based on what this microRNA itself is targeting.”
Another project funded by the Cancer Center’s “Sparking Bench-to-Bedside Team Science Project” award is building from results of this study to explore therapies for pancreatic and gastric cancer. The investigators are exploring the tumor microenvironment, in particular the immune cell MDSCs, referred to previously, that appears to dampen the chemotherapeutic response to immunotherapies.
The project relies heavily on Dr. Zavros’ “BioDroid” program, which develops miniature organs in the lab with a realistic microanatomy, also known as organoids. These are used in collaboration with the Tissue Acquisition Repository for Gastrointestinal and HEpaTic Systems (TARGHETS), created by Dr. Merchant. TARGHETS is a GI/Hepatology biorepository that collects samples from patients who undergo endoscopy.
Both Drs. Zavros and Merchant are looking to the BioDroid and TARGHETS efforts to reveal additional information that will allow them to develop new approaches to address resistance of gastric cancer to immunotherapies.
“We want to find a way to reprogram the cancer cells or the immune cells within that patient's tumor environment to make the patient more responsive to the therapy,” Dr. Zavros said. “A biomarker gives us a place to start.”
# # #
Another version of this article appeared originally on the Tomorrow Is Here webpage of the UArizona Health Sciences website.
NOTE TO EDITORS/WRITERS: Photo and video assets associated with this article are available here – https://arizona.box.com/s/h56jdpby60nlx564aiu1f0ap7ymvaquo.
About the University of Arizona Cancer Center
The University of Arizona Cancer Center is the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center with headquarters in Arizona. The UArizona Cancer Center is supported by NCI Cancer Center Support Grant No. CA023074. With primary locations at the University of Arizona in Tucson and at Dignity Health St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center in Phoenix, the Arizona Cancer Center has more than a dozen research and education offices throughout the state, with more than 300 physicians and scientists working together to prevent and cure cancer. For more information: cancercenter.arizona.edu (Follow us: YouTube).
About the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson
The University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson is shaping the future of medicine through state-of-the-art medical education programs, groundbreaking research and advancements in patient care in Arizona and beyond. Founded in 1967, the college boasts more than 50 years of innovation, ranking among the top medical schools in the nation for research and primary care. Through the university's partnership with Banner Health, one of the largest nonprofit health care systems in the country, the college is leading the way in academic medicine. For more information, visit medicine.arizona.edu (Follow us: Facebook | Twitter | Instagram | LinkedIn).
About the University of Arizona Health Sciences
The University of Arizona Health Sciences is the statewide leader in biomedical research and health professions training. UArizona Health Sciences includes the Colleges of Medicine (Tucson and Phoenix), Nursing, Pharmacy, and the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, with main campus locations in Tucson and the Phoenix Biomedical Campus in downtown Phoenix. From these vantage points, Health Sciences reaches across the state of Arizona, the greater Southwest and around the world to provide next-generation education, research and outreach. A major economic engine, Health Sciences employs nearly 5,000 people, has approximately 4,000 students and 900 faculty members, and garners $200 million in research grants and contracts annually. For more information: uahs.arizona.edu (Follow us: Facebook | Twitter | YouTube | LinkedIn | Instagram).

